Residronate: What it is and how it helps your bones
Residronate is a bisphosphonate medicine used to strengthen bone and lower the risk of fractures. Doctors most often prescribe it for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men at higher fracture risk. It can also be used to treat low bone density caused by certain medical conditions or medicines.
How residronate works and who might get it
Residronate slows the breakdown of bone by reducing activity of cells that dissolve bone tissue. That lets bone rebuild and stay stronger over time. If you’ve had a fracture from low bone density, or your bone density scan shows thin bones, your clinician may suggest a bisphosphonate like residronate.
It’s not for everyone. People with certain esophagus problems, low calcium, or severe kidney disease usually shouldn’t take it. Tell your doctor about dental issues, upcoming dental work, or pregnancy plans before starting residronate.
How to take residronate safely (simple rules)
Many users take residronate once a week. Here are practical tips that cut the chance of common problems:
- Take the pill first thing in the morning with a full glass (8 oz) of plain water. Don’t use coffee, juice, or mineral water.
- Stay upright (sit or stand) for at least 30 minutes after the dose. Lying down increases the risk of throat or esophagus irritation.
- Wait at least 30 minutes before eating, drinking, or taking other medicines, supplements, or calcium. Calcium and some antacids reduce absorption.
- If you miss a weekly dose, follow your prescriber’s rule—usually take it the next morning, but never take two doses on the same day.
Common side effects include stomach upset, heartburn, and mild muscle or joint pain. Most are mild and go away. There are rare but serious risks to know about: irritation or damage to the esophagus, unusual thigh or groin pain that may signal a rare fracture, and very rarely, jaw problems after dental surgery. Report severe chest pain, trouble swallowing, black stools, or persistent thigh pain right away.
Your doctor may ask for periodic bone density scans and blood tests for calcium and kidney function. If you need dental work, tell your dentist you take a bisphosphonate—sometimes timing matters.
If you’re considering residronate, talk openly with your clinician about benefits and risks for your specific case. Ask how long you should stay on it and what follow-up checks you’ll need. Small lifestyle steps—enough calcium and vitamin D, regular weight-bearing activity, and quitting smoking—add a lot to bone health alongside any medicine.
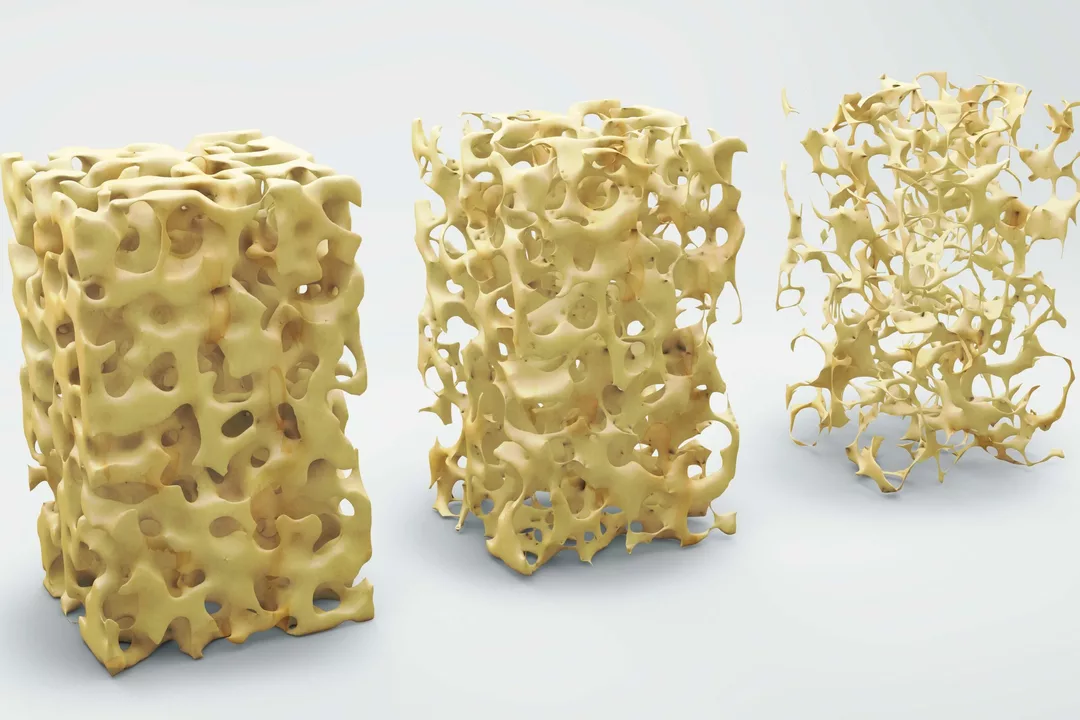
The Connection Between Residronate and Bone Mineral Density
In my recent research, I discovered a significant connection between Residronate and Bone Mineral Density (BMD). As a medication primarily used to treat osteoporosis, Residronate has proven to be effective in increasing BMD and reducing the risk of fractures. It works by slowing down the process of bone loss, allowing the body to maintain and even improve bone strength. However, it's important to follow the prescribed dosage and consult with a healthcare professional to avoid potential side effects. Overall, Residronate plays a crucial role in managing and improving bone health in individuals with low BMD.
