Understanding Bone Mineral Density and Residronate
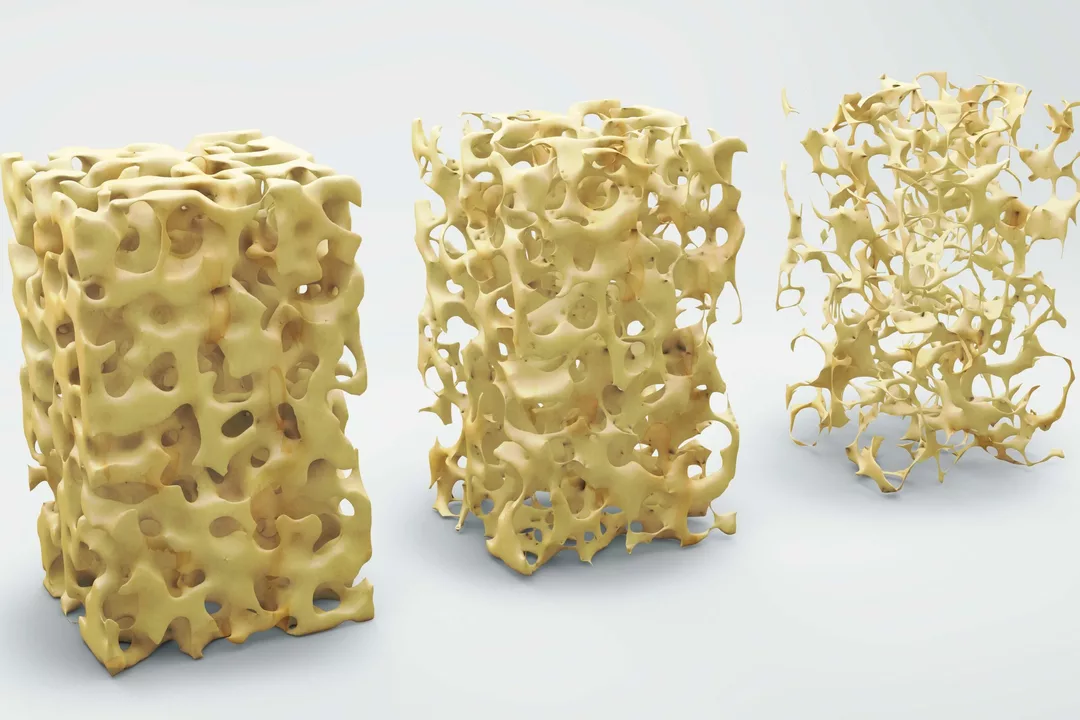
Before diving into the connection between Residronate and bone mineral density, it is important to first understand what bone mineral density is and how it plays a role in our overall health. Bone mineral density, or BMD, refers to the amount of mineral content in our bones. This measurement is used to determine the strength and health of our bones, with higher BMD levels indicating stronger bones. Residronate is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs called bisphosphonates, which are commonly prescribed to treat various bone-related conditions, such as osteoporosis and Paget's disease. In this article, we will explore how Residronate affects bone mineral density and the benefits of using this medication for bone health.
The Mechanism of Residronate in Strengthening Bones
Residronate works by inhibiting the activity of osteoclasts, which are cells responsible for breaking down bone tissue. This process, known as bone resorption, is a natural part of our body's bone repair and maintenance system. However, when bone resorption occurs at a faster rate than bone formation, it can lead to a decrease in bone mineral density and an increased risk of fractures. By suppressing the activity of osteoclasts, Residronate helps to slow down bone resorption, allowing the bone-building cells, called osteoblasts, to catch up and create a more balanced bone remodeling process. This, in turn, leads to an increase in bone mineral density and overall bone strength.
Residronate's Effectiveness in Osteoporosis Treatment
Osteoporosis is a common bone disease characterized by low bone mineral density, making bones more susceptible to fractures. Residronate has been proven to be an effective treatment option for individuals with osteoporosis, as it helps to increase bone mineral density and reduce the risk of fractures. Studies have shown that individuals who take Residronate for osteoporosis treatment experience a significant increase in their BMD levels, particularly in the spine and hip regions, which are the most common fracture sites in osteoporosis patients. Additionally, Residronate has been shown to reduce the risk of vertebral fractures by up to 50%.
Improvement in Bone Pain and Other Symptoms
Apart from increasing bone mineral density and reducing fracture risk, Residronate has also been found to improve bone pain and other symptoms associated with bone-related conditions. Bone pain can be a debilitating symptom for individuals with osteoporosis or Paget's disease, significantly impacting their quality of life. By slowing down bone resorption and promoting healthier bone remodeling, Residronate can help alleviate bone pain and improve overall bone health.
Monitoring Bone Mineral Density during Residronate Treatment
When undergoing treatment with Residronate for any bone-related condition, it is important for healthcare providers to closely monitor the patient's bone mineral density levels. This is typically done through a bone density scan, also known as a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan. This noninvasive test helps doctors to track changes in BMD levels over time and determine the effectiveness of the treatment. Regular monitoring of BMD levels during Residronate treatment ensures that the medication is working as intended and allows healthcare providers to make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Residronate's Safety and Potential Side Effects
Residronate is generally considered to be a safe and well-tolerated medication for most individuals. However, as with any medication, there are potential side effects that may occur during treatment. Some common side effects of Residronate include gastrointestinal issues, such as stomach pain, heartburn, and nausea. More serious side effects, although rare, can include jawbone problems and unusual fractures of the thigh bone. It is essential to discuss any concerns about potential side effects with your healthcare provider and to report any unusual symptoms or side effects as soon as possible.
Conclusion: The Importance of Residronate for Bone Health
In conclusion, Residronate is a valuable medication for individuals with low bone mineral density or bone-related conditions, such as osteoporosis and Paget's disease. By inhibiting the activity of osteoclasts and promoting a more balanced bone remodeling process, Residronate helps to increase bone mineral density, reduce the risk of fractures, and improve bone pain and other symptoms. Regular monitoring of BMD levels during Residronate treatment is crucial for ensuring the medication's effectiveness and maintaining optimal bone health. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new medication and discuss the potential benefits, risks, and side effects associated with Residronate.

Comments
Darla Sudheer
April 29, 2023 AT 05:20Thanks for breaking down how Residronate works on bone density. It’s good to see a clear explanation of osteoclast inhibition and the benefits for spine and hip health. I’ve been on the drug for a year and my latest DXA scan showed a modest gain in BMD. The side‑effects mentioned, like mild stomach upset, are something to watch for. Overall, the article makes the treatment sound pretty accessible.
Elizabeth González
April 29, 2023 AT 05:23The mechanistic overview aligns with current pharmacological understanding of bisphosphonates. By modulating the remodeling equilibrium, the agent facilitates a net accrual of mineralized matrix. Nonetheless, longitudinal surveillance via densitometry remains indispensable to substantiate therapeutic efficacy.
chioma uche
April 29, 2023 AT 06:20Our ancestors built stronger bones without relying on foreign concoctions, and we should demand indigenous solutions.
Satyabhan Singh
April 29, 2023 AT 07:20Residronate, a nitrogen‑containing bisphosphonate, exerts its therapeutic effect primarily through the inhibition of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase within osteoclasts, thereby precipitating apoptosis of these resorptive cells. This biochemical interference curtails the pathological acceleration of bone turnover that characterizes osteoporosis and related skeletal disorders. The resultant shift in the remodeling balance permits osteoblasts to dominate the bone formation phase, leading to measurable increments in bone mineral density as confirmed by dual‑energy X‑ray absorptiometry. Empirical data from randomized controlled trials indicate that lumbar spine BMD can increase by up to fifteen percent after two years of adherence, a magnitude that translates into a clinically meaningful reduction in vertebral fracture incidence. Moreover, hip BMD improvements, though more modest, contribute to a lowered risk of femoral neck fractures, which are notably morbid in the elderly population. It is noteworthy that the drug’s anti‑resorptive potency is contingent upon proper administration protocols, including fasting and upright posture, to mitigate gastrointestinal irritation. Patient education, therefore, assumes a pivotal role in optimizing both safety and efficacy outcomes. From a cultural perspective, the acceptance of such pharmacotherapy varies across societies, with some populations expressing reservations rooted in historical medical experiences. In regions where traditional bone health practices predominate, integrating bisphosphonate therapy necessitates respectful dialogue and evidence‑based counseling. The ethical imperative to balance pharmacologic intervention with cultural sensitivity cannot be overstated. Additionally, the rare but serious adverse events, such as osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical femoral fractures, underscore the necessity for vigilant monitoring and judicious patient selection. Clinicians are advised to reassess the risk‑benefit profile periodically, particularly after five years of continuous exposure, in accordance with contemporary guideline recommendations. In summary, while Residronate offers a robust mechanism for augmenting bone mineral density, its deployment must be accompanied by comprehensive patient education, regular densitometric evaluation, and an appreciation of individual cultural contexts. Only through such a holistic approach can the full therapeutic potential of the medication be realized, thereby enhancing skeletal health on a global scale.
Keith Laser
April 29, 2023 AT 08:00Wow, another miracle pill that promises to turn our spines into steel – because diet and exercise clearly aren’t enough, right? It’s comforting to know that popping a tablet once a week can magically patch up every micro‑fracture accumulated over decades. Of course, we’ll just gloss over the occasional jaw issues and hope the benefits outweigh the hype. Let’s all celebrate the convenience while ignoring the fact that lifestyle changes still matter. Cheers to modern medicine’s easy fixes!